Dr. Tin Tin Cho
ဒေါက်တာဒေါ်တင်တင်ချို
Position : Professor(Head)
Degree : B.A, M.A, Ph.D
Philosophy
Teacher list
| Sr.No | Department | Name | Position | Education | Thesis Title | Field Of Specialization | Current Research Project | Email/Gmail |
| 1 | Philosophy | Dr. Tin Tin Cho | Professor(Head) | Ph.D | A Philosophical Study of The Concept of Reality in Buddhist Tradition of Pyu | Culture | – | [email protected] |
| 2 | Philosophy | Daw Hla Hla Maw | Associate professor | M.A | Myanmar Proverb and their ethical foundations of Myanmar’s Way of Living | Ethics | – | [email protected] |
| 3 | Philosophy | Daw Aye Aye Cho | Associate professor | M.Res | A Study of Personal Virtues and Social Virtues in Buddhist Ethics | Ethics | – | [email protected] |
| 4 | Philosophy | Daw Khin Thida Aung | Lecturer | M.Res | A Critical View on Confucius’ Ethics | Ethics | – | [email protected] |
| 6 | Philosophy | U Thet Ko Win | Tutor | M.A | A Critical Study Of Spinoza’s Deterministic Ethics | Ethics | – | [email protected] |
| 7 | Philosophy | Daw Naw Cinderella | Tutor | M.A | A Comparative Study of Rationalism and Empiricism | Ethics | – | [email protected] |
| 8 | Philosophy | Daw Ei Kay Khaing Kyaw | Tutor | M.A | A Critical Study Of Four Cardinal Values In Buddha’s Teaching | Ethics | – | [email protected] |
| 9 | Philosophy | Daw Aye Aye Moe | Tutor | M.A | A Study on Four Noble Truths of Buddhism | Ethics | – | [email protected] |
| 10 | Philosophy | U Hein Htet | Tutor | M.A | A Study of the Nature of Human Existence In Soren Kierkegaard’s Thought | Ethics | – | [email protected] |
Programmes Offered
- B.A. / B.A. (Hons) in Philosophy
- M.A. and M.Res. in Philosophy
Curriculum
B.A. in Philosophy
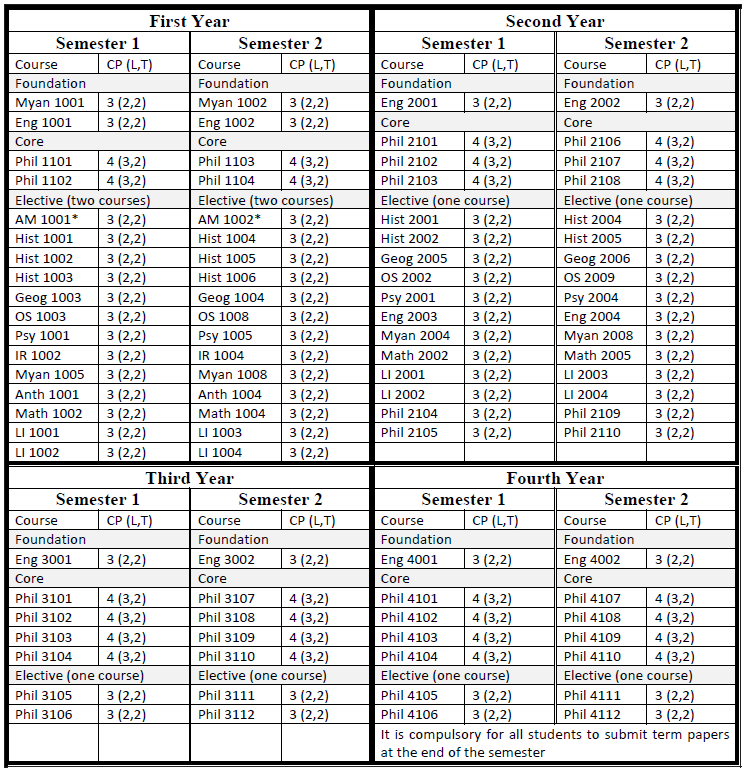
B.A. (Honours) in Philosophy
Students who passed second year with GPA greater than 4 are eligible to attend B.Sc. (Honours) classes for three more years. After finished successfully, they are earned B.Sc. (Hons) degree majoring in Philosophy.
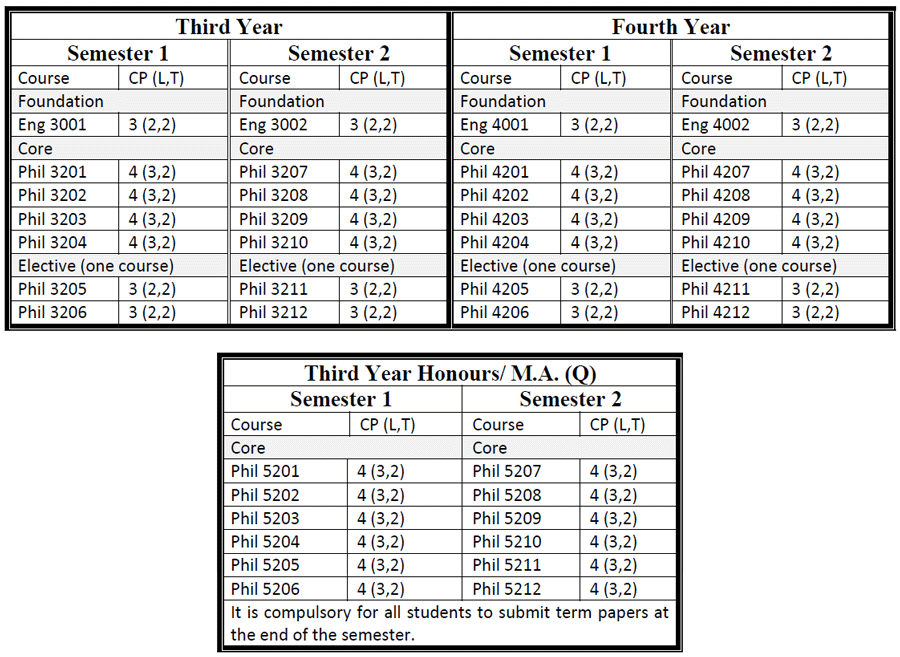
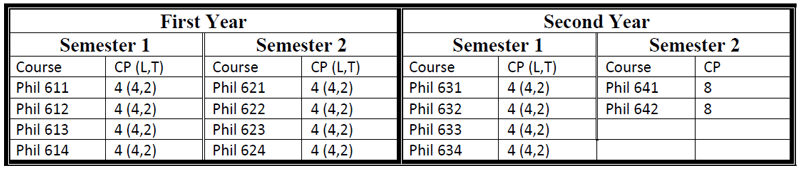
M.A. in Philosophy
Course Descriptions
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to distinguish between valid and invalid reasoning. You have to study, in the first semester, the Meaning of Logic, Logical Fallacies, and Propositions. In the second semester, you have to study Categorical Syllogism, Mixed Syllogism, Mediate Inference, Poly-Syllogisms, Sorities, Epicherima, Enthymemes and the Utility of Deductive Logic for daily life-problem solving.
The purpose of this subject is to enable to examine critical thinking of Western Philosophy. You have to study, in the first semester, the development of Early Greek Philosophy, Plato’s Philosophy and Aristotle’s Philosophy. In the second semester, you have to study Medieval Philosophy, Modern Philosophy, and German Idealism.
The purpose of this subject is to enable to distinguish valid and invalid reasoning in daily life as elective course for other specialization.
The purpose of this subject is to enable to examine Myanmar Culture and Myanmar Society, Western Moral Views from the aspects of Myanmar Moral Thought, Myanmar Moral Values, Myanmar’s View on Human Existence, Truth and Human Values as elective course for other specialization.
The purpose of this subject is to enable to examine the Nature of argument, Theory of Truth Functions, the Method of Deduction, Quantification Theory (Propositional Functions and Quantifiers), Propositional Calculus, Class Calculus and Boolean Expansion for students of Mathematics specialization.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine the synthetic ways of thinking of Eastern Philosophy. You have to study, in the first semester, characteristic of Indian Philosophy, stages and development of Indian Philosophy and a general survey of Indian Philosophical systems. In the second semester, you have to study characteristic and schools of Chinese Philosophy and evaluation.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine logical thinking. You have to study, in the first semester, the nature of Induction, some subsidiary processes of Induction, basic Principles of Induction, different kinds of Induction, some new theories of Induction, evaluation of Inductive reasoning, criteria for causal determination , and the utility of inductive logic for daily life. In the second semester, you have to study evaluation of Mill’s method of causal determination, the nature of Inference in science, study of scientific methodology, and views regarding scientific methodology.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine the development of contemporary philosophy and its general characteristics, Bergson’s Ontology and Epistemology, Pragmatism of C. S Peirce, James, Dewey, Schiller, Logical Positivism of A. J. Ayer and R. Carnap and Realism of G. E. Moore, Bertrand Russell and G. Santayana. In the second semester, you have to study Analytical Philosophy, Existentialism, Contemporary Western Idealism, later Twentieth Century philosophy, evaluation of Contemporary Philosophy and Postmodern Thought.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine Environmental Conservation, the need for an ethics of environmental conservation, and Environmental Ethics as a topic of Applied Ethics. In the second semester, you have to study Ethical views on environmental conservation and the new ecological world view and the Teachings of Theravāda Buddhism. This course is also offered to Psychology students.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine Natural Law of St. Thomas Aquinas, Logical Positivism of J. Austin, Legal Realism of J.C. Gray, A New Positivist Conception of law of H. L. A. Hart and The Problems of the Valuation of Law. In the second semester, you have to study Law and Morality, Justice and Value of Right. This course is also offered to Law students.
The purpose of this subject is to enable for students of English specialization to examine western intellectual development of ways of thinking on social, political and philosophical ideas from Greek to Modern period.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine the Nature of Aesthetics, Aesthetics and Art Criticism, critical study of western Aesthetical theories, Modern Aesthetics: Romanticism, Art for Art’s sake Movement, Emotionalism, Veron, Collinwood , Tolstoy, Formalism, and Realism. In the second semester, you have to study some Eastern Aesthetic Theories of Indian, Chinese, Japanese and Myanmar.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine the Nature of argument, Theory of Truth Functions, the Method of Deduction, Quantification Theory (Propositional Functions and Quantifiers). In the second semester you have to study an Evaluation of Mill’s Method of Causal Determination, The Nature of Inference in Science, Study of Scientific Methodology, Francis Bacon’s conception of Scientific Method, Cohen and Negel’s Conception of Scientific Method and John Dewey’s view of Scientific Method.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine philosophical study of history such as truth and fact in history, the notion of objectivity in history, Determinism and Freedom in history. Then you have to study some nineteenth century historical theories Kant’s conception of history and Herder’s conception of history. In the second semester you have to study some historical theories of Hegel, Marx, Tolstoy, Spengler, Toynbee E.H. Carr and Toffler.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine influence of Buddhism on Myanmar Thought, Myanmar Culture and Myanmar Literature. Then, you have to study Philosophical impact on Myanmar Traditional Festival, Myanmar Thought on Reality, Myanmar Thought on Knowledge and Myanmar Thought on Morality. In the second semester, you have to study Myanmar View on Cause and Effect. Natural Law and Social Law, the Law of Kamma, Ledi Sayadaw’s View on Causation. Then you have to study Humanism in Myanmar Literature, Myanmar Philosophical View on History and Myanmar Thought on Morality.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine selection from ancient Western philosophy of Heraclitus, Plato and Aristotle. Then you have to study selection from Descartes, Hume, Kant, Hegel, Nietzsche, Russell, James and Ayer. In the second semester you have to study selections from the Indian Philosophy of Tagore, Gandhi, Radhakrishnan and Chinese Philosophy of Confucius , Lao Tzu and Mo Tzu. Then you have to study selections from Japanese Philosophy of D. T. Suzuki, Kitaro Nishida and Watsuji. Then, you have to study selections from Myanmar Literature.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine the nature and scope of ethics and ethical problems. Then you have to study some Western ethical theories of Ancient Greek Ethics, Utilitarianism, Sociological Ethics, Evolutionary Ethics, Kantian Ethics, The Ethics of G.E. Moore, The Ethics of John Dewey, The Ethics of A.J. Ayer and Existentialist Ethics. In addition, you will get a chance to study ethical approach to instill awareness of the need for environmental conservation. In the second semester you have to study the Eastern Ethics of Indian, Chinese and Japanese. Moreover, Ethics and Practical Problems of life, Freedom and Moral Responsibility, Right and Duty, and Myanmar Theravada Buddhism and Ethics of Environmental Conservation will be studied.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you in the first semester to examine analytical and critical study of Philosophy of Religion and in the second semester you have to study a comparative study of Religion.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine the Nature of Philosophical Problems, epistemological problems such as problems of Intuition, problem of perception and problem of truth. In the second semester, you have to study Ontological problems such as problem of Being and Becoming, problem of Substance, ethical problem, problem of human nature, problem of Individual and society, and, problem of human freedom and determinism.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you in the first semester to examine the development of science and technology from Greek to Contemporary times, Logic and Methodology of Science. In the second semester you have to study Method of Science, Philosophical Problems of Science and Problem of Some Basic Concept of Science.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine research methodology in Philosophy that prepares to write a term paper.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine contemporary Indian Philosophy, Chinese Philosophy and Japanese Philosophy to analyze ways of eastern thinking and culture.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine political ideas and concepts from Greek to Modern period.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you in the first semester to examine issues in Indian Philosophy and in the second semester you have to study issues in Chinese Philosophy.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine problem of Reality, Pre-Socratic Materialists, Early Nonphysical Views of Reality, Plato’s Forms Aristotle’s Metaphysics, Metaphysics of Descartes, Spinoza and Leibnitz. In the second semester you have to study Philosophies of Process of Bergson, Dewey and Whitehead Moore and the Revival of Realism, Egoism versus Altruism, Duty – defined Morality, -Kant and the Authority of Reason, Utilitarianism: Bentham and Mill, Nietzsche and the Attack on Morality.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine Background of Buddhism, Life of the Buddha, Historical sketch of Buddhism. In the second semester you have to study Schools of Buddhist Thought, Main Themes of Buddhist Teachings, Philosophical Concepts in Buddha’s Teachings, Aesthetic Evaluation of Buddhist Arts.
The purpose of this subject is to enable you to examine Plato’ View on Knowledge and Virtue. In the second semester you have to study Aristotle’s View on Knowledge and Virtue.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA first year student in the first semester to examine formal logic and research methodology. You have to study Truth Functional Analysis, Derivations and Models, Derivations, Quantificational Logic (Theory of Quantification: Predicate Logic) and research methodology.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA first year student in the first semester to examine nature of Social Philosophy, a Brief Study of the Origin and Development of Social Philosophy Ancient Egypt, China, Japan, India, Greece, Rome, Social Philosophy in the Middle Ages, a Critical Study of Some Theories of Modern Social Philosophy Michiavelli, Vico, Hobbes, Locke. Hume, Voltaire, Rousseau, a Critical Study of Some Theories of Twentieth Century Social Philosophy of Dilthy, Collingwood, Northrop, Jaspers, Hegel and Karl Marx, Some Sociological Problems in Social Philosophy and the Value of Social Philosophy.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA first year student in the first semester to examine application of aesthetic theories on art, a critical examination of some problems of aesthetics on art- Form and Content, Act and Freedom, Art and Society, Art and Symbolism, Function of art, Art and Realism, Art and Romanticism, A Study of the art and other areas of human concern-Art and Religion , Art and Education, Art and Society ,and , Research study of Myanmar views on art and aesthetics.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA first year student in the first semester to examine Consequentialist Ethics, Deontological Theories of Morality, Ethics Extracted From Lokaniti Written by the Minister Caturingabala, Ethics of Mahatma Gandhi, Ethics of Rabindranath Tagore, The Criticism of W.E. Frankena and other Philosophers on the Ethics of G.E. Moore and the Concept of Free Will and Responsibility in the Ethics of A. K. Stout.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA first year student in the second semester to examine some Problems of Formal Logic, Inductive Inferences and Theory of Probability, Deontic Logic, Logic in Theravada Buddhism, and Philosophical Logic.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA first year student in the second semester to examine Existentialism and the History of Philosophy, the Idea of Existence, Existentialist outlook of History and Culture, Conflicting thoughts on History among Existentialist, Existentialism, Literature, and Arts, Existentialism, Psychology and Theology, a detailed study of Kierkegaard or Jaspers or Heidegger or Sartre or Camus, A Study of Phenomenology, The Meaning of Phenomenology, A Study of Heidegger and Phenomenological Method , and , A Study of Sartre and Phenomenological Method.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA first year student in the second semester to examine Historical Development of the Philosophy of Science of Kant, Mill, Whewell, March, Duhem, Carnap and Popper, and Empirical foundation of science, Rational foundation of science, Metaphysical foundation of science, Methods of the Natural Sciences, Methodological Problems of the social sciences, Scientific Law and Theory, Space, Time and Causality.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA first year student in the second semester to examine nature of philosophy of history, some philosophers’ views on History, Explanation in History, Determinism and Indeterminism in History.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA second year student in the second semester to examine Scientific Definition of Culture, Facts and Values in Culture, Empirical study of Culture, Deductively formulated theory of culture.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA second year student in the second semester to examine Shinto and Japanese Culture, Zen Buddhism, and Korean Philosophy.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA second year student in the second semester to examine A philosophical Study of Some Traditional Myanmar festivals, The Nature of Pure Fact in Myanmar Thought, The Conception of Art and Knowledge in Myanmar Culture, The concept of man in Myanmar Thought, Traditional Culture in Myanmar Society, The Concept of Mangala and Contemporary Myanmar, The Concept of Mangala and its Relevance in Contemporary Times, The Concept of Mettā and its Cultural Reality in Myanmar, Milinda’s Dilemmatic Arguments in Myanmar Thought.
The purpose of this subject is to enable MA second year student in the second semester to examine Philosophy of Bertrand Russell, Philosophy of George Santayana, Philosophy of Whitehead, Philosophy of John Dewey and Postmodern Thought of Michel Foucault, Jacques Derrida and Richard Rorty.