Dr.Kyawt Hmu Aung
ဒေါက်တာဒေါ်ကြော့မှူးအောင်
Position : Professor(Head)
Degree : B.A (History), M.A.(History), M.A. (Archaeology )Ph.D (Archaeology)
Archaeology
Position : Professor Degree : B.A (I.R). M.A. (Archaeology )Ph.D (Archaeology)Dr.Yin Myo Thu ဒေါက်တာဒေါ်ယဥ်မျိုးသူB.A (I.R). M.A. (Archaeology )Ph.D (Archaeology)
Teacher list
| Sr.No | Department | Name | Position | Education | Thesis Title | Field Specialization | Current Research Project | Email/Gmail |
| 1 | Archaeology | Dr. Kyawt hmue Aung | Professor (Head) | Ph.D | Decorative Buddist Arts Of Bagan | Buddhist Art (Bagan to Kongbaung Period) | Bagan | [email protected] |
| 2 | Archaeology | Dr. Yin Myo Thu | Professor | Ph.D | Religious Dedication of King Narapatisithu | Historical Archaeology | Role of Terracotta in Myanmar archaeology | [email protected] |
| 3 | Archaeology | Daw Thidar Nyein | Associate Professor | M.A | Architecturalworks of Pyu cities Beikthan Hlain, Sriksetra | Protohistoric and Early Historical Archaeology in Myanmar | The Study on stone stulpture in Sriksetra | [email protected] |
| 4 | Archaeology | Daw Aye Aye Moe | Associate Professor | M.A | _ | Historical Archaeology | _ | [email protected] |
| 5 | Archaeology | U Zin Maung Oo | Associate Professor | M.A | Arts and Architecture of Pheiklake Temple | Art and Architecture of Bagan Temple | Excavation at Lattpan | [email protected] |
| 6 | Archaeology | Daw Khin Than Aye | Associate Professor | M.A | The Study of Pakhon Gyi Area | Historical Archaeology | The Study On Twantay Township | dawkhinthanaye [email protected] |
| 7 | Archaeology | Dr. Ni Mar Myo | Lecturer | Ph.D | Buddha Images In Bagan Period | Historical Archaeology | _ | [email protected] |
| 8 | Archaeology | Daw Sandar Myint | Tutor | M.A | Arts and Architecture of Shwe Inn Pin Monestery | Historical Archaeology | _ | sandar.myint [email protected] |
| 9 | Archaeology | Daw Khaing Wah | Tutor | M.A | Arts and Architecture of Mae Nu Ouok Kaung | Historical Archaeology | _ | [email protected] |
| 10 | Archaeology | Daw Chan Mya Mya Aung | Tutor | M.A | Arts and Architecture of Maha Budhi Temple at Bagan | Historical Archaeology | _ | chanmya0998252gmail.com |
| 11 | Archaeology | Daw Ingyin Myo | Tutor | M.A | Mural Painting of Myinkaba Kubyauk Gyi Temple at Bagan | Historical Archaeology | _ | [email protected] |
| 12 | Archaeology | Daw Myat Min Min Soe | Tutor | M.A | Mural Painting of Abeyadana Temple at Bagan | Historical Archaeology | _ | [email protected] |
Programmes Offered
- B.A. / B.A. (Hons) in Archaeology
- M.A. and M.Res. in Archaeology
Curriculum
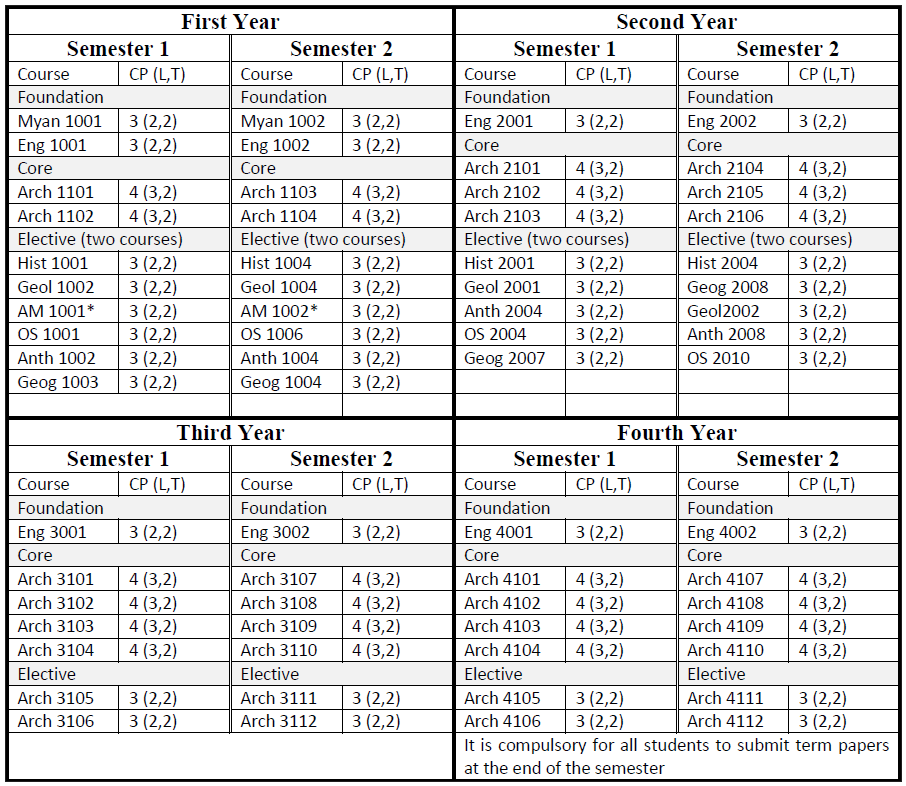
B.A. in Archaeology
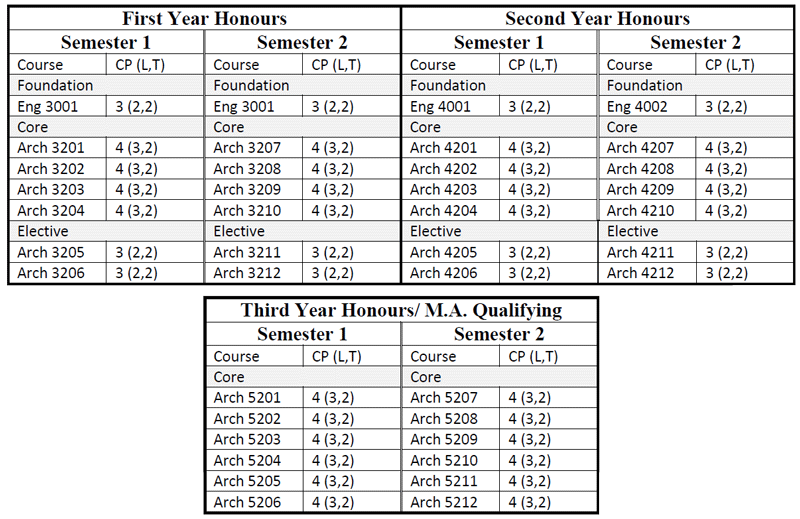
B.A. (Honours) in Archaeology
Students who passed second year with GPA ≥4 are eligible to attend B.A. (Honours) classes for three more years. After they finished successfully, they earned B.A. (Hons) degree in Archaeology.
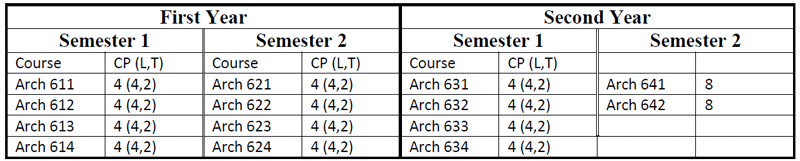
M.A. in Archaeology
Course Descriptions
Archaeology is the study of the past using object and other excavated evidences as the main source of data. This module includes the definition of archaeology, framework of archaeology, evolution theory and field archaeology, prehistoric archaeology, protohistoric archaeology, historical archaeology, and ethic of archaeology or protecting cultural heritages.
Myanmar was a land mass extending from Myitkyina down to the Kayah state. There were certainly erosion and great earth movement which caused valleys and mountains to appear. These movements had happened 700-800 million years ago. Taninthayi area was left out of the sea in about 160 million year ago. Rakhine Yoma appeared 60 million years. Mingun-Mandalay region was 40 million. In this module, students will learn pondaung, primate in Myanmar, Stone Age Culture, Bronze Age Culture and Iron Age Culture
Archaeological sites are places where traces of human activity are to be found. In this module, you can learn archaeological sites, classifying sites, common kinds of sites, how archaeological sites become buried, how sites are destroyed, how sites are discovered. It also deals with Surface signs of archaeological remains and Utilizing Evidences Sequences in stratigraphy and typology.
Theoretically, urbanization is defined by such factors as organization of human resources, centralized control of man power, large scale architecture work including defended and irrigation system, increased population, settlement pattern of towns and cities. So, the Early Urban societies coincided with these characteristic features in the archaeological landscape of Myanmar are those of Pyu in the inland region, Economic structure and social structure of Early Myanmar- Cultural Status of Beikthano, Halin and Sriksetra and Rakhine civilization.
The technique of the field archaeology is based on study of survey, preliminaries, how site are discovered, how site are located. It also covers excavation of system lay-out system, grid system, interpretation of archaeological finds or post excavation analysis, survey and stratification photography.
The module will introduce to Hinduism, Brahmanism, Vishnuism, Shivaism and Jaimism. It also covers other Hindu gods: Indra, Surya and Usher. Indra was the god of rain, stream and war. Surya the sun-god, Angi was the god of fire and Usher was the goddess and dawn.
The module is about the fundamental of stone tools technology, how to extract raw material of stone from mines and quarries of ancient time, the basic technique for manufacturing stone tools, technique of the old world stone industries and types of ground stone tools. Stone tools are made by removing material from a pebble or core tail in order to get the desired shape of the core. Although the core is the main implement, the flakes themselves may well be used as knives, scrapers etc. The first recognizable tools are simple choppers and flakes made by knocking pieces off pebbles to obtain sharp edges.
In the second half of the twentieth century, several scientific dating methods have dramatically altered and have been developed. Of all the methods, radio carbon helps the archaeologists to establish for the first time a reliable chronology of world cultures. Archaeology of dating methods are seriation, palynology, archaeomagnetism, varve analysis and potassium organ dating.
Hinduism became a powerful religion. The Hindu were worshippers of Shiva and Vishnu since the worship of Shiva and Vishnu became very popular. It was believed that Vishnu sometimes came to earth to help them. Hindu image of gods were placed in temples. The earliest examples of religious architecture in India are attributed to Asoka. The earliest known temple is Sanchi.
Myanmar Neolithic implements (the small size and narrow blades of some adze) were obviously the cutting tools of woodcutter. Classifications of stone tools are chipped tools, edge-ground tools and completely ground tools. Most of the tools are made on pebble. Later, they were made by silicified tuff, vein quartz and fossil wood.
This module is about the earliest Buddhist art and architecture, the architectural style of stupas in ancient India, earliest, classical and localization period of Buddhist monuments in Myanmar and the sculptures of the life of Buddha.
The old world consists of Africa, Europe and Asia whereas North and South America are considered as the new world.
The name of Southeast Asia came into use during the Second World War. The vast area of Southeast Asia is composed of eastern mainland of Asia forming the Indo-Chinas peninsula and huge archipelago including Indonesia and the Philippines. The former consists of Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam and Malaysia, Later Indonesia, Brunei Sarawak, North Bormeo, Timor and Singapore. The students will also study about early hunter-gatherer communities, costal settlement, expansion of settlement, the expansion of domestic communities, Bronze age and Samon valley culture of ancient Southeast Asia.
The invention of writing has had a greater influence in uplifting the human race than any other achievement in the life of the man. Egyptian inscription known as Hieroglyphic began in 4700 BC. But some suggest that Egyptian alphabet: 24 Hieroglyphic letters or signs were earliest alphabets known. The Chinese started using ideograms from about the years of 5000 BP. Indus valley people of Mohenjodaro and Harappa used some kinds of pictorial writing form about 2800 years B.P. In Myanmar Pyu would have used the kadamba scripts and Gupta scripts of the 4th century AD. Mon used the Pallava Script also of the 4th century AD although the earliest Mon writing in terracotta of the 7 century AD. Myanmar learnt the art of writing in about 11th century AD.
Ceramics artifacts, made from stone tools are the most durable objects created by prehistoric peoples. Technically, ceramics are things made from materials which are permanently changed when heated. There are three types of ceramic in the archaeological record: earthenware, stoneware and porcelain, all are made from clay. Ceramics are not limited to utilitarian wares and they include fine wares for ceremonial functions and trade as well as other types of objects such as figurines, jewelry and even toys. The art of manufacturing pottery was discovered about 12,000 years ago in the Old World and about 5,000 years ago in the New World. Pottery is also a reflector of the social and physical environment in which it was made and used, and is therefore an indicator of change in social traditions and social patterning. It is an important resource for interpreting the past.
The human image of the Buddha does not occur during the early centuries of Buddha. The Buddha is incomparable and in this sense human representation of his likeness is not permissible. This ideological prohibition remained for more than five hundred years after the death of the Buddha. Later, Buddha images have developed after Buddhist schools are appeared. Countries where Buddhism is practiced in Asia are Indonesia, Indochina, Cambodia, Nepal, Myanmar, Srilanka and Thailand.
Archaeology of Europe includes the foundation of European civilization and Archaeology of Asia includes the Indian sub-continent and Harappan civilization on the Indus valley Asia, Southeast Asia, India and Pakistan, South and East Asia, China and Japan.
In Southeast Asia, the BronzeAge began within the period 1500-1000BC. These sites are Bac Bo Area, Chao Phraya Plain, Khorat Plateau and Mekhong Valley. Autonomy and chiefdoms, development of Mandalas, Culture of Pyu, Angkorian Mandala and culture of Bagan are very important of Southeast Asia.
The definition of antiquities was mentioned in the Ancient monument and antiquities preservation act of 1957. Antiquities mean any archaeological object which was made before 1886 January and the land where the archaeological objects exist. Archaeological objects include the following items:- fossilized bone of man or animal, manmade cave, dwelling place, monument or their rims, any religious, ritual residential, palace building, natural cave or rock shelter, ancient artifacts, ancient paintings, carving, sculptures, ancient writing on stone, wood, paper palm-leaf, parabeik, any art object which is declared by the government as antique.
In the history of glazed ceramic, there are two distinct technological traditions. Glazed tradition originated in the Middle East before 1100BC and in China in 1500 BC. In Myanmar, Pyu people used glazed bricks for their very long city walls about 802 AD. In fact, the reliable evidences to glaze ceramic traditions in Myanmar came from Bagan Period. Later, Pyu people used clay tablets, votive tablets and burial urns.
Archaeological Survey of India was established in 1862. But a clear picture of the growing interest in archaeological studies originated about 70 years before. It was in 1783 when Sir William Jones came to Calcutta as Pusine Judge of the Supreme Court. He learnt Sanskrit, and had the idea of the foundation of an institution for promoting the study of oriental literature and culture.In1784, a meeting was held at Calcutta and decided to found a society with the object of enquiring the history and antiquities, arts sciences and literature of Asia.
Though China has an ancient Civilization, it was only in the 1920s that archaeology began to develop to fill out the story of that civilization. Chinese archaeologists have carried out extensive investigations, excavations and research an ancient tombs, sites and cultural relics with excellent results. China proper is made up chiefly of two great rivers: the Yellow and the Yangtze and one smaller one, the Hsi Kiang, which, taking their rise in the vast tablelands, and mountain fastnesses to the west, flow eastward into an arm of the Pacific. The Sinanthropus like Pithecantropus of Homo-erectus is also known as Peking Man. The site of Sinanthropus was placed Chou-Kou-tien cave near the village about 54 km (16miles) to the South-Wast of Peking. Homo-erectus lived during the Middle Pleistocence, about half a million years ago. The topography of the Pekings area in the Pleistocene was different from that of today. The others contained the deposits of Sinanthropus who occupied the region in the Middle Pleistocene about 500,000 years ago. The countryside abounded with other mammals such as ancient horses, pigs, deer, buffaloes, sabre-toothed, tigers, cats as large as lions and many others. The list of Chou-K’ou-tien fauna totals 118 types, ninety-four of which are a mammal with thirty extinct species.
This module covers about the first immigrant of the New World, the first inhabitant of Eastern Siberia, the first human settlement of north American, the earliest stone tool tradition of north America, the culture of Palaeo-Indian, the expension of settlement in north America (west, east), the first agriculturalists in the New World, the culture sequence at Tehuacan Valley in central Mexico and the Maya civilization.
This paper covers about the origin of coins, money before coinage, the birth of coin money, the invention of coin money, the history of monetary system of Sumerian metal, Kydian, Iorian, Carthaginian, Etruscan, Greek and Roman, and also the ancient Chinese and Indian coins. Numismatology is the study of ancient collection of currency including coins, medals tokens, paper money and related objects used as coin money: copper, alloy, silver, gold and other.
This module covers the stone age of European, types of stone tools, traces of their permanent structures, the Mesolithic culture of hunter-fishers, the basic technology of Mesolithic Europe, the findings of the hunter-fishers from Palaeolithic and Mesolithic, the initial zone of European agriculture, the late stone age farmers, their first and second expansion to middle and west Europe, the earliest metallurgy in Europe, middle Europe and Iberia, the Aegean World, Aegean Palace civilization, Minoan-Mycenaean civilization, the late bronze age of crete, and the beginnings and early development of Greek religion.
In this chapter, we can study that the development of Indian Museums, museums of the department of Archaeology, National museum of India, Archaeological Museum, Epigraphical Research, Epigraphy of India, Early Indian Epigraphy, Scripts used in Indian and scripts abroad, language of the inscription, preservation of inscriptions and publication.
Geographically and culturally, South China is comparable to the Upper Yaungtze. The whole region is distinctly hilly and mountainous with limited of level land. As world Palaeolithic archaeology has engaged in the debate between “the out -of- Africa” and “the multiorgional-development” schools, evidence from China has become crucial. The majority of Chinese archaeologist and paleontologist support the multiregional development model, arguing for an independent system of evolution from Homo erectus to Homo sapiens in East Asia. Some have gone even further and attempted to find evidence of the earliest hominid in China.
Native Americans were the first humans to inhabit these regions, arriving thousands of years before European exploration of the new world. Native American of middle and south American and diversity of cultural areas: Mesoamerical culture, the Caribbean and Northern Andes Culture, central and South Andes Cultural and Culture of New Zealand.
The term “museum” originated from the word “muse”, related to Greek word. Actually, the term “muses” is early used by English and referred to the churches of ancient Greek, Egypt and Roman Period where the paintings were collected. A museum may collect anything but it cannot collect everything. The principle function of the museum is not only to collect, maintain and display the objects but also to show the evolution of the works of art of human being, processes of the traditional art up to the current stage in order to promote the educational knowledge. This module will familiarize the students with the beginning of Museology, Museum of the world and museum in Myanmar.
The origins of one of the world’s earliest complex societies in the land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Mesopotamia is one of the cradles of human civilization. Here, the earliest cities in world history appeared about 3500 BC. Language and writing, agriculture, information of forming, Sumerian script, religion and ancient city of Uruk were appeared at Mesopotamia.
“Archaeology is anthropology or it is nothing” is a statement with which many archaeologists would strongly agree. As a statement of disciplinary identity, it is odd contradictory and not at all straight forward. Instead, we are indicating that archaeology is a branch of Anthropology, composed of archaeology, social, cultural anthropology, physical anthropology which study all aspects of human life, past and present.
This module will familiarize the students with the nature of plant and plant remains, clarifying the subsistence pattern, nutrition and diet of prehistoric people, pollen analysis, what they ate in ancient time, micro botanical remains, interpreting the context and remains, analysis of plant residues on artifacts, seasonally and domestication of plants and plant evidences from literate societies.
Underwater archaeology is the discipline that studies past human life, behavior and culture using the physical remains found in salt or fresh water or buried beneath water-logged sediment. It is most often considered as a branch of maritime archaeology. Underwater archaeology is not necessarily under bodies of water. It also includes archaeology of dried up river bed, sand banks, sand bass lakes, streams and shallow seas.
Cognitive archaeology can be defined as the study of “the ways that ancient societies thought as inferred from material remains”. Archaeologists have always been interested in the “thought behind the artifacts”. Cognitive archaeology as a distinct field is a relatively new development as outgrowth of processual archaeology. It currently relates with a range of related fields including palaeoanthropology, animal ethology, evolutionary psychology, artifacts intelligence, neuroscience and cognitive science.
The human body is a superb machine which is capable of actions, requiring strength and force, and others involving fine control and specialization skills. However, this is not always the case. How do we trace the development of various human abilities?
Archaeologists from different times used various criteria to indentify and distinguish the rich from the poor within a community, these include paucity or wealth of all tomb-goods, paucity or wealth of certain specified type of tomb-goods, separate areas of cemeteries and standardization of burial custom, size of funerary construction, and the indirect evidence of physical remain.